In a groundbreaking discovery, scientists have identified a new lanternfly species Vietnam Cambodia, expanding our understanding of the biodiversity in Southeast Asia. Lanternflies, known for their vibrant colors and intricate patterns, belong to the family Fulgoridae and play essential roles in their ecosystems. This newly documented species not only highlights the rich biodiversity of the region but also underscores the importance of conservation efforts to protect these delicate habitats.
New Lanternfly Species Vietnam Cambodia: Nature’s Winged Beauties
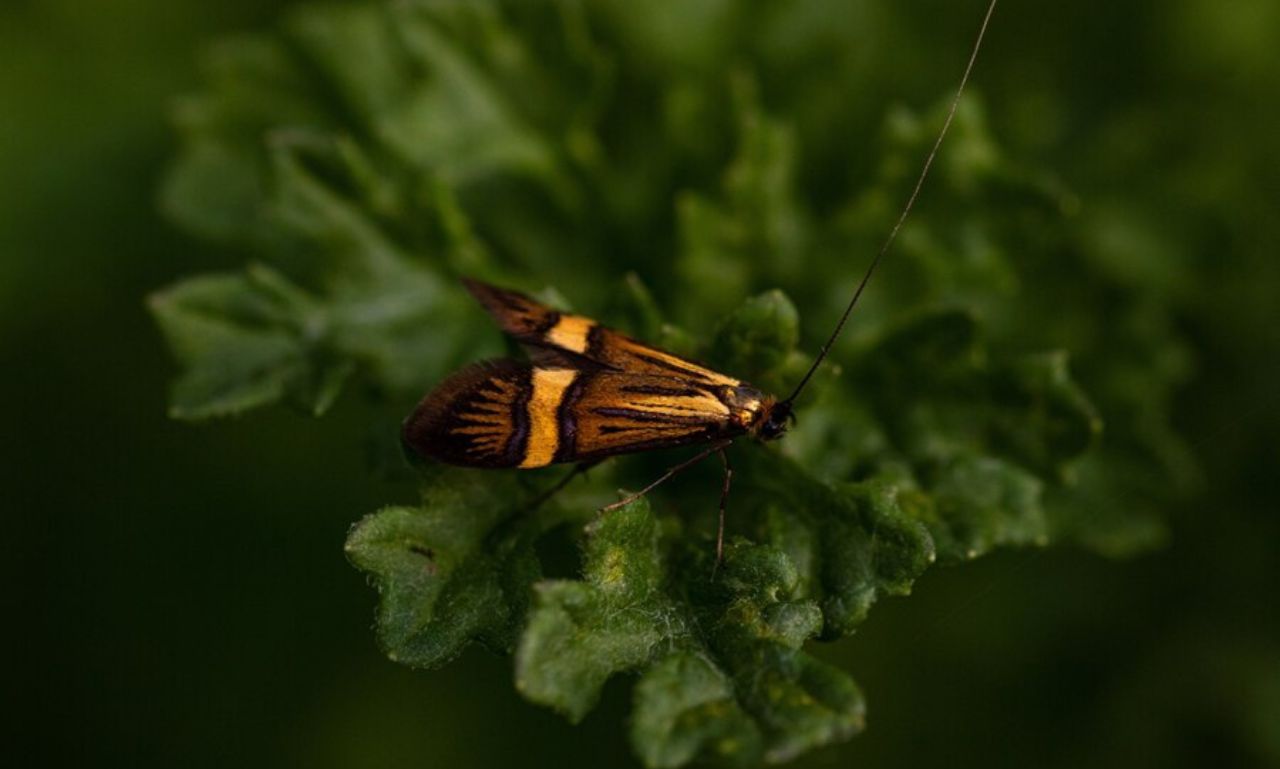
New lanternfly species Vietnam Cambodia are a group of planthoppers that are often mistaken for moths or butterflies due to their colorful and elaborate wings. Despite their name, lanternflies do not emit light; the term “lantern” likely originates from the bulbous shape of their heads, which in some species resembles a lamp.
Key Characteristics of Lanternflies
- Size: Most lanternflies measure between 2 to 4 inches.
- Coloration: They exhibit stunning patterns and colors that serve as camouflage or warning signals.
- Diet: Lanternflies feed on plant sap using their piercing-sucking mouthparts.
Details of the New Lanternfly Species Vietnam Cambodia
The new lanternfly species discovered in Vietnam and Cambodia showcase unique features that distinguish it from other known species.
Physical Description
- Wings: The species exhibits a blend of vibrant hues, such as deep oranges and iridescent blues, with intricate vein patterns.
- Body Structure: Its elongated body and distinct head shape set it apart from other members of the Fulgoridae family.
Habitat and Range
- Found primarily in tropical forests, the species thrives in regions with abundant vegetation and high humidity.
- Researchers have documented its presence in Vietnam’s Annamite Mountains and Cambodia’s Cardamom Rainforest, areas known for their rich biodiversity.
Ecological Role
- As sap feeders, lanternflies contribute to the nutrient cycling of ecosystems.
- They serve as prey for birds, lizards, and other predators, playing a crucial role in food chains.
Significance of the Discovery
This discovery highlights the untapped biodiversity of Southeast Asia, a region already recognized as a global hotspot for endemic species.
Scientific Insights
- The lanternfly’s genetic makeup offers valuable data for understanding the evolutionary relationships within the Fulgoridae family.
- Comparative studies could shed light on how environmental factors influence lanternfly adaptation and speciation.
Conservation Implications
- The species’ habitat faces threats from deforestation and agricultural expansion.
- Protecting these ecosystems is critical not only for lanternflies but also for countless other flora and fauna sharing the same environment.
Challenges in Documenting New Species
Discovering and classifying new species is a painstaking process that requires time, resources, and expertise.
Threats to Habitat
- Deforestation in Vietnam and Cambodia is reducing the available habitat for many species, including lanternflies.
- Climate change poses additional risks by altering the ecosystems where these insects thrive.
Lack of Resources
- Limited funding for biodiversity research hampers the ability to conduct extensive field studies in remote areas.
Uncertain Taxonomy
- Lanternflies often exhibit subtle morphological differences, making species classification challenging without genetic analysis.
Conservation Efforts for Lanternflies and Their Habitats
The discovery of this new lanternfly species underscores the urgent need for conservation in Southeast Asia.
Protected Areas
- National parks and wildlife sanctuaries in Vietnam and Cambodia, such as Cat Tien National Park and Preah Monivong Bokor National Park, are critical for preserving biodiversity.
Community Involvement
- Local communities play a vital role in conservation by adopting sustainable practices that reduce deforestation and habitat degradation.
Global Collaboration
- International partnerships between governments, NGOs, and research institutions are essential to fund and implement conservation programs.
How Lanternflies Inspire Scientific Curiosity
Lanternflies, with their stunning beauty and ecological significance, continue to fascinate scientists and nature enthusiasts alike.
Biomimicry Potential
- The structural patterns and colors of lanternfly wings inspire innovations in materials science and design.
Educational Opportunities
- Raising awareness about lanternflies can promote environmental education and inspire efforts to protect biodiversity.
FAQs About the New Lanternfly Species Vietnam Cambodia
Where was the new lanternfly species discovered?
The species was found in the tropical forests of Vietnam and Cambodia, particularly in biodiversity-rich areas like the Annamite Mountains and Cardamom Rainforest.
What makes this lanternfly species unique?
Its vibrant coloration, distinct wing patterns, and specific habitat preferences differentiate it from other known species in the Fulgoridae family.
Why are lanternflies important to ecosystems?
Lanternflies contribute to nutrient cycling by feeding on plant sap and serving as prey for various predators, maintaining ecological balance.
What are the main threats to this species?
Deforestation, habitat destruction, and climate change pose significant threats to the survival of this species.
How can we protect lanternflies and their habitats?
Supporting conservation initiatives, protecting forests, and involving local communities in sustainable practices are key to preserving their ecosystems.
Are lanternflies harmful to humans or crops?
Lanternflies are not harmful to humans, but some species can become pests by feeding on crops. However, there’s no evidence that the new species poses such a risk.
Conclusion
The discovery of a new lanternfly species Vietnam Cambodia is a testament to the region’s incredible biodiversity and the importance of conserving its natural habitats. As researchers delve deeper into its characteristics and ecological role, this find serves as a reminder of the delicate balance in nature and our responsibility to protect it.
Preserving these unique ecosystems not only safeguards the lanternfly but also ensures the survival of countless other species, enriching our planet’s natural heritage for future generations.









zj5c9z
1f36qs
39id57